Specialists in Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments
Treatment of Neuropathies
Specialised treatment
At Vitalys Centre, we offer specialised treatments for peripheral neuropathies using advanced neuromuscular physiotherapy, with the aim of:
○ Reducing nerve pain and improving sensitivity.
○ Restore muscle strength and coordination.
○ Improve motor function and overall mobility.
○ Slow progressive deterioration and improve quality of life.
Peripheral Neuropathies
What are neuropathies and how do they affect your quality of life?
Peripheral neuropathies are disorders that affect the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. They manifest themselves with pain, tingling, muscle weakness, loss of sensation and difficulty moving, affecting the arms, legs, hands or feet. The most common causes include diabetes, nerve compression, trauma, infections, or side effects from medications.
These alterations in nerve conduction can limit the patient’s autonomy and cause chronic discomfort if not treated correctly.
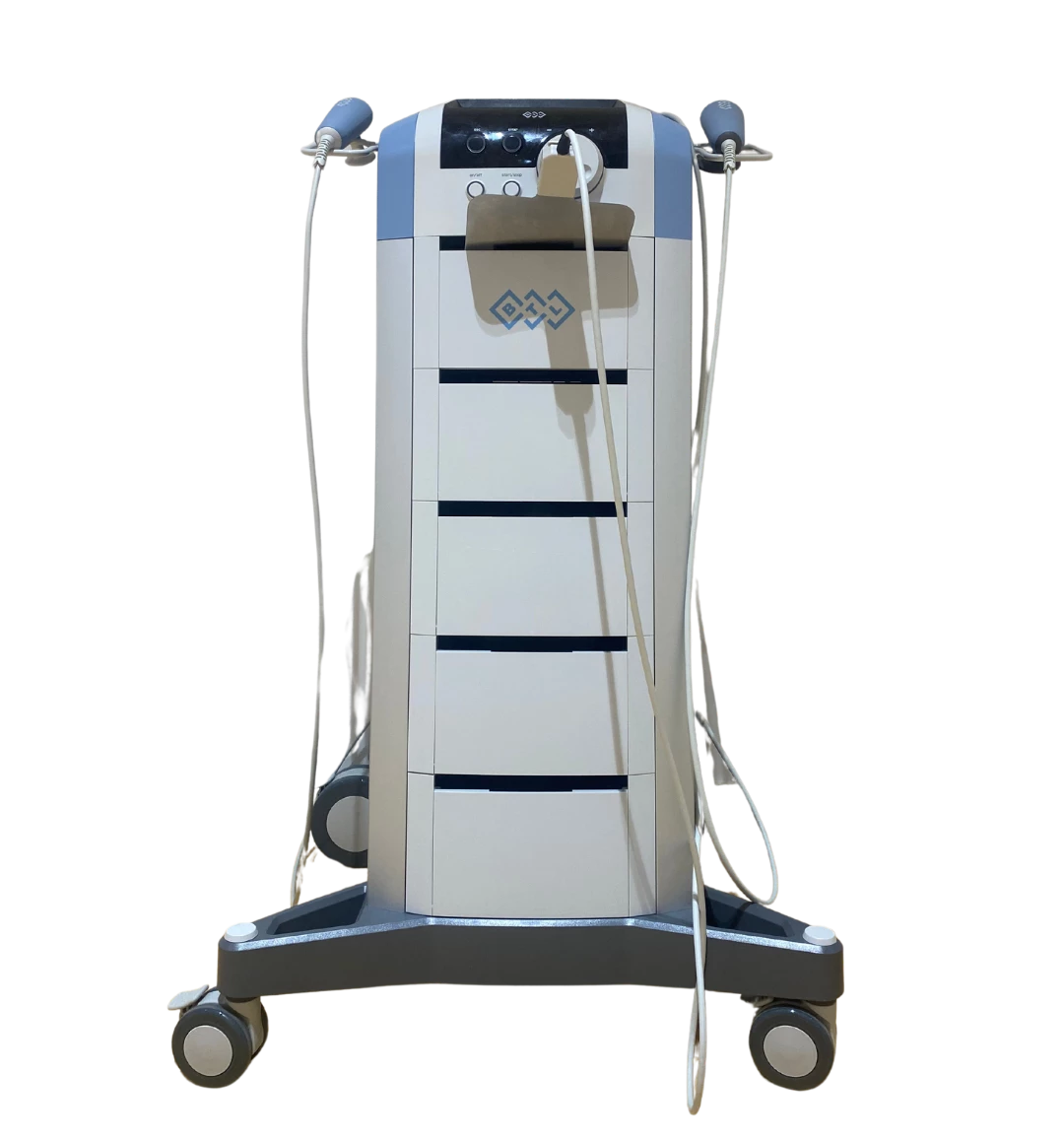
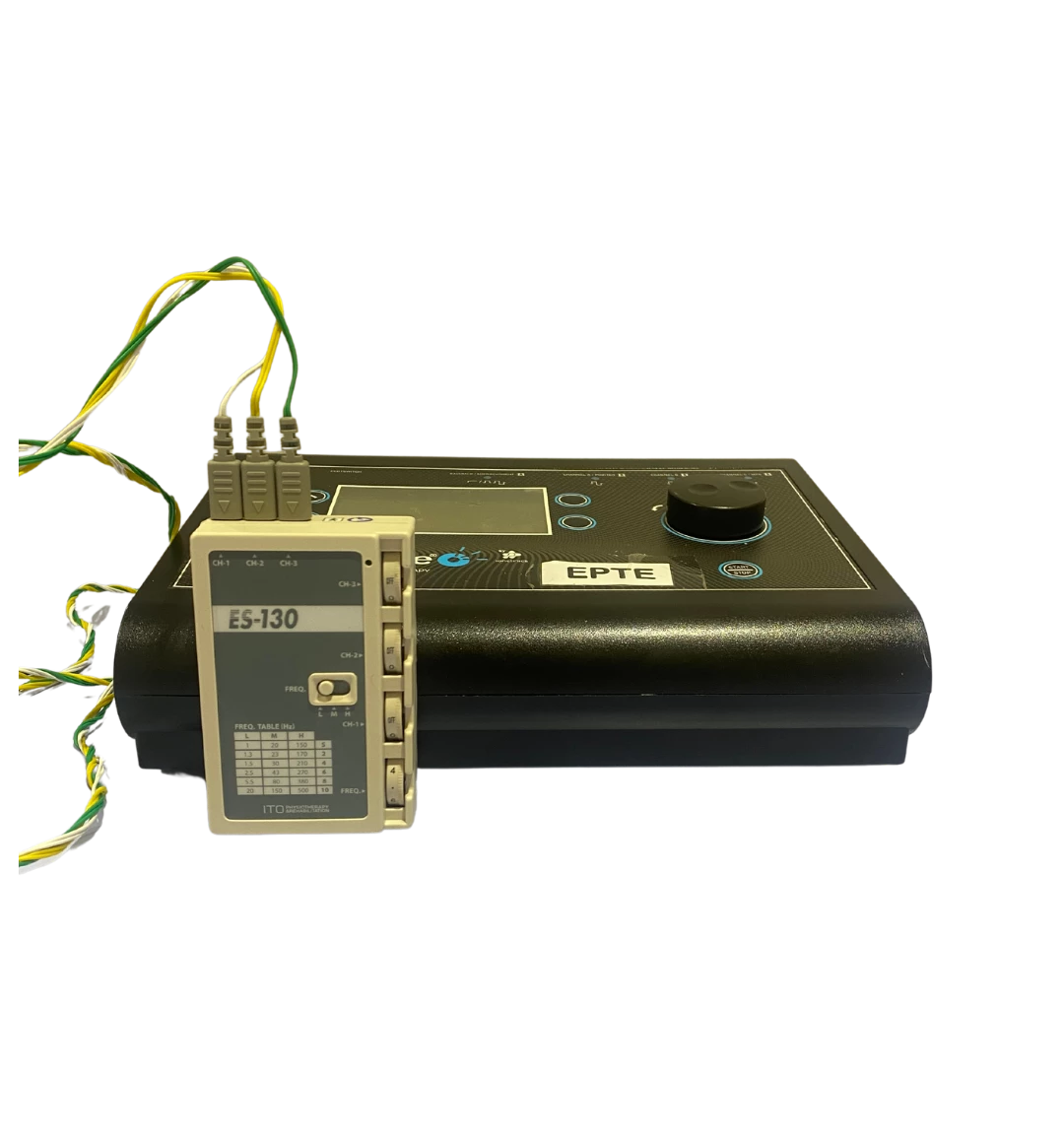
Some of the technologies we use in our treatments
Physiotherapy for neuropathies
Effective, non-invasive, evidence-based treatment
Physiotherapy is one of the most effective and safest tools for treating peripheral neuropathies, both sensory and motor. Through an individualised and non-invasive approach, it helps to reduce nerve pain, restore muscle function and improve sensitivity in the affected areas.
Physiotherapy not only treats the symptoms of neuropathy, but also addresses the mechanical and neuromuscular causes that trigger or aggravate it, achieving real and sustainable improvement over time. This type of treatment is especially useful in the early stages of neuropathy, but it also offers relief and functionality in chronic or advanced cases, preventing progressive deterioration and improving the patient’s quality of life.
What types of neuropathies do we treat with physiotherapy?
We treat sensory, motor and mixed neuropathies associated with:
Carpal tunnel syndrome.
Sciatica or lumbar radiculopathy.
Nerve entrapment neuropathy (peroneal, ulnar, median).
After-effects of traumatic or surgical nerve injuries.
Idiopathic or inflammatory neuropathies.